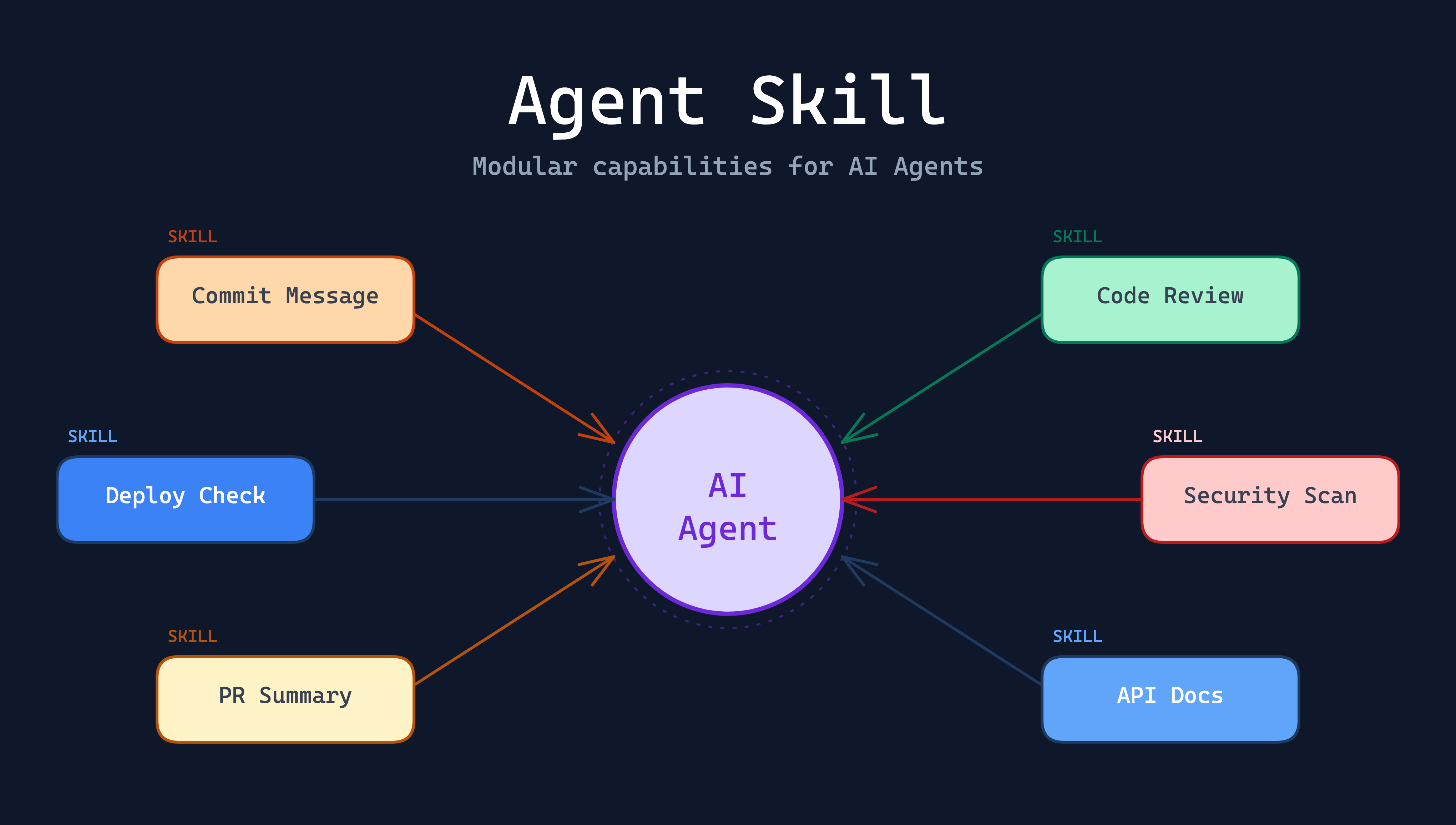
隨著 AI Agent 技術的快速發展,一個全新的概念正在改變軟體開發的工作方式:Agent Skill(代理技能)。如果你有使用過 Claude Code、Cursor 或其他 AI 輔助開發工具,可能已經接觸過類似的概念。本篇文章將深入介紹什麼是 Agent Skill,以及它如何對軟體產業帶來根本性的變化。
[Read More]
隨著 AI Agent 技術的快速發展,一個全新的概念正在改變軟體開發的工作方式:Agent Skill(代理技能)。如果你有使用過 Claude Code、Cursor 或其他 AI 輔助開發工具,可能已經接觸過類似的概念。本篇文章將深入介紹什麼是 Agent Skill,以及它如何對軟體產業帶來根本性的變化。
[Read More]
With the rapid evolution of AI Agent technology, a new concept is reshaping how software development works: Agent Skill. If you’ve used Claude Code, Cursor, or other AI-assisted development tools, you may have already encountered something similar. This article takes a deep dive into what Agent Skill is and how it brings fundamental changes to the software industry.
[Read More]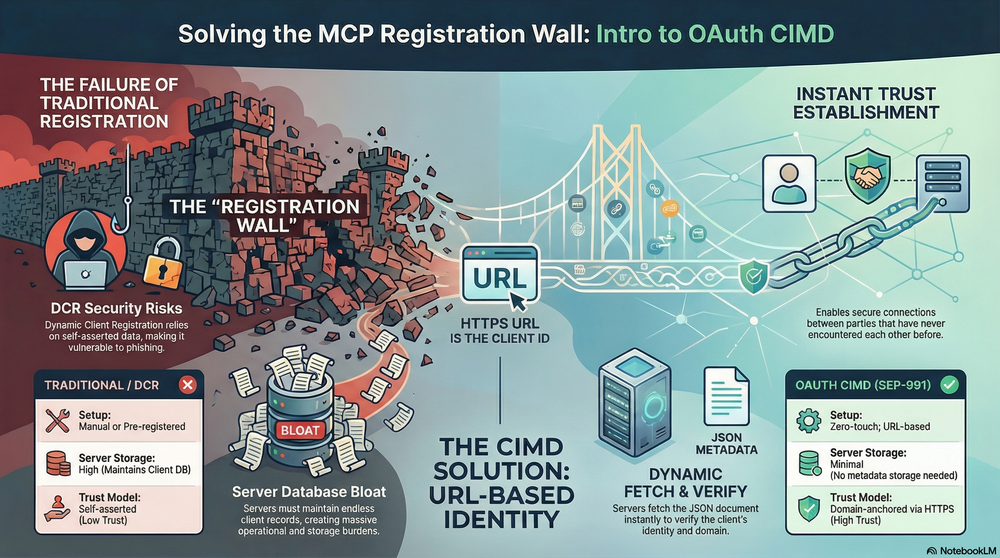
In 2025, I introduced MCP (Model Context Protocol) at the iThome Taiwan Cloud Summit. At that time, I mentioned that the official team has been continuously revising the authentication protocol to address complex authentication flows. The previous design involved DCR (Dynamic Client Registration), so as expected, on 2025/11/25, a new Authorization mechanism was released. This authentication mechanism is called “Client ID Metadata Documents, abbreviated as CIMD”.
When installing a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, the most challenging part is often not the protocol itself, but how to establish trust between the client and server. If you’ve ever tried to connect an MCP client to an MCP server it has never encountered before, you’ve probably run into what’s known as the “registration wall”.
Pre-registering with every possible authorization server is simply not scalable, and while Dynamic Client Registration (DCR) helps, it lacks reliable mechanisms to verify client identity, making it vulnerable to phishing attacks. Beyond security concerns, DCR also creates operational overhead by generating an ever-growing number of duplicate client identities that need to be managed.
[Read More]
2025 年在 iThome 臺灣雲端大會介紹過 MCP (Model Context Protocol),那時候就有提到在認證協議部分,官方其實一直都在改版解決複雜的認證流程,之前設計的 DCR (Dynamic Client Registration),所以沒意外去年 2025/11/25 又推出一版 Authorization 機制,此認證機制取名叫『Client ID Metadata Documents 簡稱 CIMD』。
安裝 Model Context Protocol(MCP)伺服器時,最棘手的部分往往不是協議本身,而是如何讓客戶端與伺服器彼此建立信任。如果你曾嘗試讓一個 MCP 客戶端連線到一個從未接觸過的 MCP 伺服器,你大概遇過所謂的「註冊高牆(registration wall)」。
要預先在每一個可能的授權伺服器完成註冊根本無法擴展,而 Dynamic Client Registration(DCR)雖然有所幫助,但因為缺乏可靠的機制來驗證客戶端身份,所以容易遭受網路釣魚攻擊。除了安全性問題之外,DCR 還會造成營運負擔,因為它會產生越來越多需要管理的重複客戶端身份。
[Read More]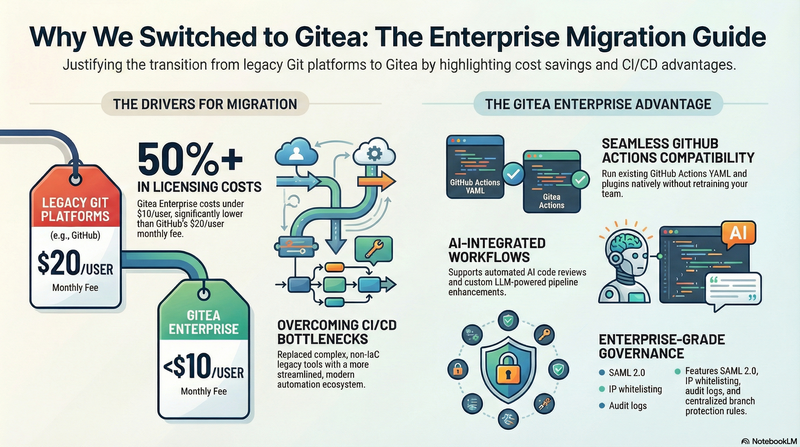
In the software development field, most people are no strangers to Git—the world’s most popular version control system and a foundational tool for modern collaborative development. And when we talk about Git, we can’t help but think of GitHub, the largest and most well-known open-source software platform today.
However, for many private companies or small to mid-sized teams, GitHub may not be an option due to security, cost, deployment strategies, or regulatory requirements. In such cases, what tools can serve as an internal Git repository platform? The most common choices include GitLab and Gitea, which is the focus of this article.
For some teams, Gitea might still be relatively unfamiliar. Simply put, Gitea is a lightweight, self-hosted Git platform written in Go, providing GitHub-like capabilities such as code hosting, permission management, Issues and Pull Requests, and CI/CD. You can find a more comprehensive explanation in the official documentation (Gitea Documentation). It’s cross-platform, easy to deploy, and low-maintenance, which is why it has been increasingly favored by small and medium-sized teams.
The main purpose of this article is to share why our team ultimately decided to migrate from Bitbucket Data Center to Gitea—and why we didn’t choose a more feature-rich but comparatively heavier open-source solution like GitLab.
[Read More]
相信在軟體開發領域,大家對 Git 應該都不陌生——這套全球最受歡迎的版本控制系統已成為現代協作開發的基礎工具。而提到 Git,就不得不想到目前全球最大且最知名的開源軟體平台 GitHub。
但在許多私人企業或中小型團隊中,如果因為安全性、成本、部署策略或法規需求等原因,而不能直接採用 GitHub,那麼有哪些工具可以作為企業內部的 Git 版本庫平台呢?最常見的選擇包含 GitLab 以及本篇將深入探討的 Gitea。
對部分團隊而言,Gitea 可能還相對陌生。簡單來說,Gitea 是一套以 Go 語言打造的極輕量、自架型 Git 平台,提供與 GitHub 類似的功能,例如程式碼託管、權限管理、Issue 與 Pull Request、CI/CD 等能力。 你也可以在官方文件中看到更完整說明(Gitea Documentation)。它跨平台、容易部署,且維護成本低,因此逐漸受到中小型團隊青睞。
本篇文章的主軸,就是要和大家分享: 為什麼我們團隊最終選擇從 Bitbucket Data Center 遷移到 Gitea?又為什麼沒有選擇 GitLab 這類功能更完整、但相對較為沉重的開源方案?
[Read More]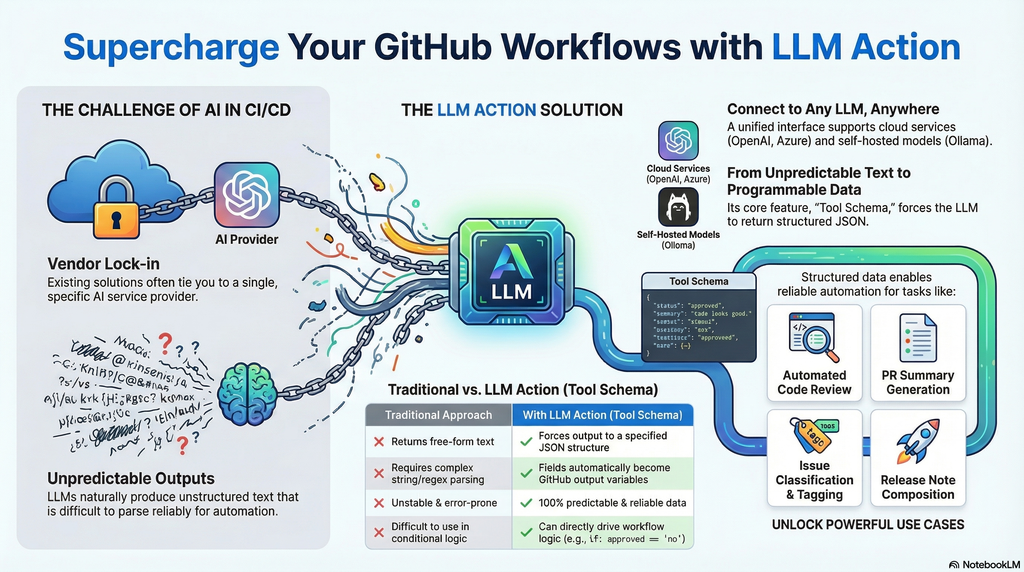
In the AI era, integrating Large Language Models into CI/CD pipelines has become crucial for improving development efficiency. However, existing solutions are often tied to specific service providers, and LLM outputs are typically unstructured free-form text that is difficult to parse and use reliably in automated workflows. LLM Action was created to solve these pain points.
The core feature is support for Tool Schema structured output—you can predefine a JSON Schema to force LLM responses to conform to a specified format. This means AI no longer just returns a block of text, but produces predictable, parseable structured data. Each field is automatically converted into GitHub Actions output variables, allowing subsequent steps to use them directly without additional string parsing or regex processing. This completely solves the problem of unstable LLM output that is difficult to integrate into automated workflows.
Additionally, LLM Action provides a unified interface to connect to any OpenAI-compatible service, whether it’s cloud-based OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, or locally deployed self-hosted solutions like Ollama, LocalAI, LM Studio, or vLLM—all can be seamlessly switched.
Practical use cases include:
score, issues, suggestions, directly used to determine whether the review passestitle, summary, breaking_changes for automatic PR description updatescategory, priority, labels to automatically tag Issuesfeatures, bugfixes, breaking to automatically compose formatted release notesThrough Schema definition, LLM Action transforms AI output from “unpredictable text” to “programmable data,” truly enabling end-to-end AI automated workflows.
[Read More]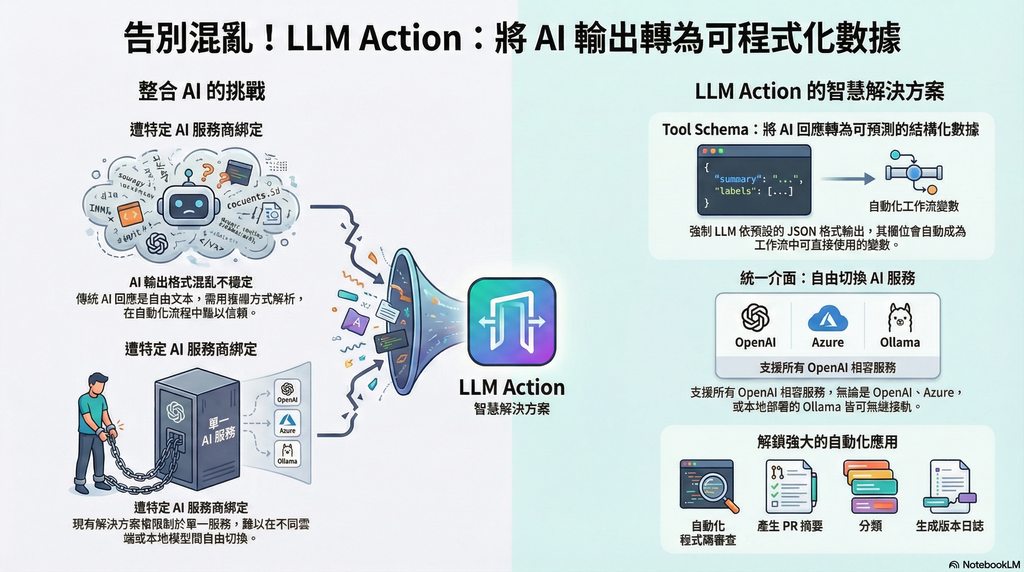
在 AI 時代,將大型語言模型整合進 CI/CD 流程已成為提升開發效率的關鍵。然而,現有的解決方案往往綁定特定服務商,且 LLM 的輸出通常是非結構化的自由文字,難以在自動化流程中可靠地解析與使用。LLM Action 的誕生正是為了解決這些痛點。
最核心的特色是支援 Tool Schema 結構化輸出——你可以預先定義 JSON Schema,讓 LLM 的回應強制符合指定格式。這意味著 AI 不再只是回傳一段文字,而是產出可預測、可解析的結構化資料,每個欄位都會自動轉換為 GitHub Actions 的輸出變數,讓後續步驟能直接取用,無需額外的字串解析或正則表達式處理。這徹底解決了 LLM 輸出不穩定、難以整合進自動化流程的問題。
此外,LLM Action 提供統一介面串接任何 OpenAI 相容的服務,無論是雲端的 OpenAI、Azure OpenAI,還是本地部署的 Ollama、LocalAI、LM Studio、vLLM 等自託管方案,都能無縫切換。
實際應用場景包括:
score、issues、suggestions 等欄位,直接用於判斷是否通過審查title、summary、breaking_changes 供後續自動更新 PR 描述category、priority、labels 自動為 Issue 加上標籤features、bugfixes、breaking 陣列,自動組成格式化的發布說明透過 Schema 定義,LLM Action 讓 AI 輸出從「不可預測的文字」變成「可程式化的資料」,真正實現端到端的 AI 自動化工作流程。
[Read More]
kubectl-ai is a revolutionary open-source project that seamlessly integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) with Kubernetes operations, enabling users to interact intelligently with K8s clusters using natural language. This article explores how this innovative technology addresses the pain points of traditional kubectl command complexity and significantly lowers the barrier to entry for Kubernetes users.
[Read More]
kubectl-ai 是一個革命性的開源專案,將大型語言模型與 Kubernetes 運維完美結合,讓用戶能夠透過自然語言與 K8s 集群進行智能交互。本文將深入探討這項創新技術如何解決傳統 kubectl 命令複雜性的痛點,大幅降低 Kubernetes 的使用門檻。
[Read More]