
Before diving in, let’s familiarize ourselves with Gitea and Jira. For better context, I recommend reading “Git Software Development Guide: Key to Improving Team Collaboration” first.
Gitea is a lightweight self-hosted Git server written in Go, providing teams with an easily deployable code management solution. It supports multiple operating systems including Linux, Windows, and macOS, while offering comprehensive features for code review, issue tracking, and Wiki management—all essential tools for enhancing team collaboration.
Jira is Atlassian’s professional project management and issue tracking system. Widely adopted by software development teams worldwide, Jira excels in issue tracking, supports agile methodologies (including Scrum and Kanban), and provides robust data analytics capabilities to optimize project management and team collaboration.
Problem Description
In our department’s development workflow, while Git serves as our version control system with Gitea as our Git server, and Jira handles our issue tracking, we faced a significant challenge: bridging the gap between code commits and Jira issues effectively.
While robust integration solutions exist for Jira with services like Bitbucket, GitHub, and GitLab, options for self-hosted Git servers like Gitea are limited. This integration challenge has been a notable discussion point in the Gitea community.
While our team discovered a Jira plugin for Git integration, its implementation approach was less than ideal. The plugin required Jira to periodically scan the Git server’s commit history to establish associations between commits and Jira issues. Although this method achieved basic integration, it was inefficient and required the Jira server to have direct access to the Git server, including downloading source code to retrieve historical records. This setup posed security concerns, particularly in large enterprise environments like ours, where departments operate under strict data access policies, making this integration method unsuitable.
To overcome these limitations, our team developed a custom Gitea-Jira integration solution that prioritizes both efficiency and security. We implemented a design where the Gitea service proactively establishes associations between commits and Jira issues, eliminating the need for Jira to access the Gitea server directly. This architecture not only significantly improves performance but also maintains data security. The implementation is straightforward, primarily leveraging Gitea Action in combination with the Jira API. Here’s an illustration of the integration:
By incorporating Jira issue numbers in commit logs, developers can seamlessly track related commit content within Jira issues, significantly enhancing the efficiency of code tracking and management processes.
Design Process
Before implementation, we established a clear mapping between our software development workflow and Jira states to ensure comprehensive progress tracking. Our workflow is structured around these essential states:
- Backlog: Pending issues awaiting prioritization
- Open: Issues ready for development
- In Progress: Issues actively being worked on
- Code Review: Code undergoing peer review
- Under Test: Issues in testing phase
- Resolved: Successfully completed issues
- Closed: Finalized and verified issues
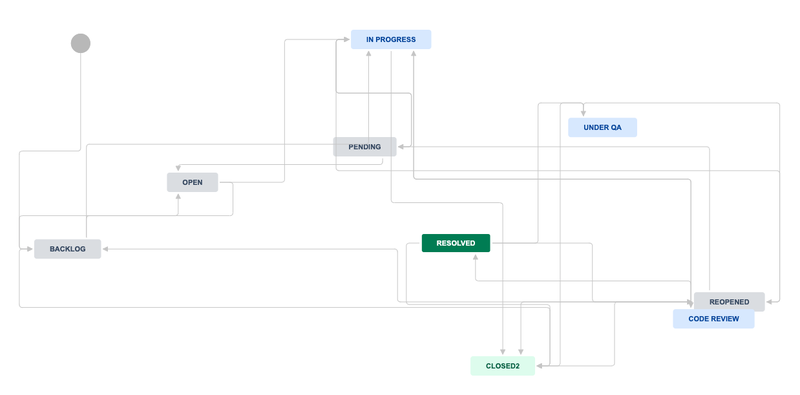
This framework provides a foundational software development process that teams can customize based on their specific requirements. Each issue progresses through distinct states, allowing developers to take appropriate actions at each stage. This structured approach ensures efficient tracking and management of the development process. We’ve established the following key state transitions that align with our Git workflows:
- Backlog → In Progress: Initiated when a new development branch is created
- In Progress → Code Review: Triggered when code is submitted for review
- Code Review → Resolved: Completed when code review is approved
To maintain workflow efficiency, we require our development team to strictly adhere to these processes. Through automated Git commit integrations, Jira issue states are updated automatically, creating a streamlined and automated development pipeline.
Integrating Jira with Gitea Action
We selected Gitea Action as our integration tool for its native functionality and comprehensive support for Git operations. It offers flexible integration capabilities while maintaining robust event handling. For detailed technical implementation, please refer to the appleboy/jira-action project.
Creating New Branches
| |
This YAML configuration automatically integrates Gitea Action with Jira. Upon branch creation, the system updates the corresponding Jira issue status to “In Progress” and assigns it to the branch creator. Within the configuration, the ref parameter captures the new branch name, the transition field defines the target Jira state, and the assignee parameter determines the issue owner.
Committing Code
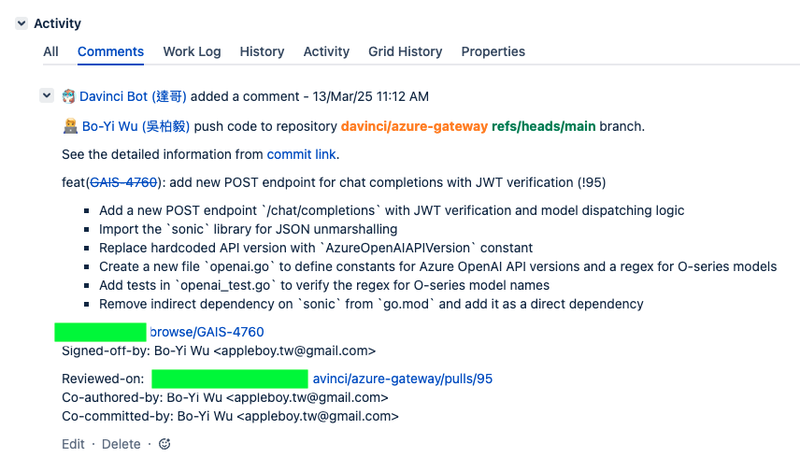
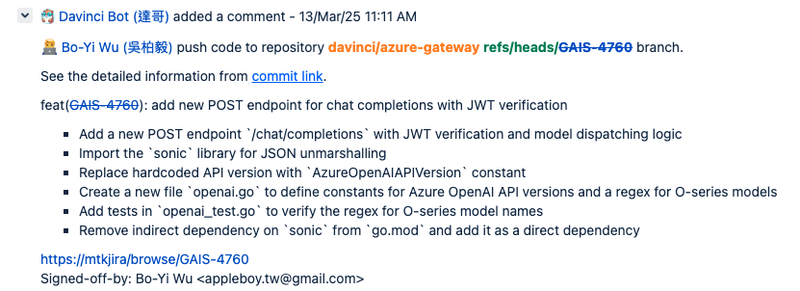
To maintain traceability, developers must include the relevant Jira issue number (e.g., GAIS-123) in their commit messages. This practice enables the system to automatically create and maintain associations between code commits and their corresponding Jira issues.
| |
When a Push Event is received, Action automatically extracts the Jira issue number from the commit message, updates the corresponding Jira issue status to In Progress, and assigns it to the committing developer. Furthermore, Action adds a detailed comment to the Jira issue containing the commit information.
Submitting Code for Review
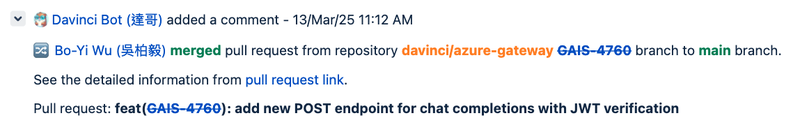
The system actively monitors Pull Request status changes (opened and closed) and automatically transitions the associated Jira issue to the “Code Review” state.
| |

Code Review Completion
The system continuously monitors Pull Request status changes and automatically transitions the corresponding Jira issue to Resolved when it detects a Pull Request has been closed. This automated workflow ensures immediate synchronization between code review completion and issue tracking.
| |
Beyond these state transitions, the system can be customized to meet specific needs, such as automatically sending email notifications when code reviews are approved or triggering test environment deployments after code merging. These automated processes enhance tracking and management of the development workflow. Gitea Action’s greatest strength lies in its versatility in handling various events, making it an exceptionally flexible integration solution.
Conclusion
Our integration implementation has successfully bridged Gitea and Jira, creating a seamless workflow that enhances both efficiency and security. Developers simply need to reference Jira issue numbers in their commit messages, and the system automatically handles all necessary associations.
In our current project, a team of 20 developers has effectively managed nearly 5,000 issues over two years, processing an average of ten new issues daily. Such volume would be challenging to manage without our automated solution.
This integration has not only streamlined our issue management but also optimized our entire development process. By eliminating manual Jira status updates, we’ve significantly improved efficiency while reducing human error. The success of this integration demonstrates the essential role of automation tools in effectively managing large-scale software development projects.