In the software development field, most people are no strangers to Git—the world’s most popular version control system and a foundational tool for modern collaborative development. And when we talk about Git, we can’t help but think of GitHub, the largest and most well-known open-source software platform today.
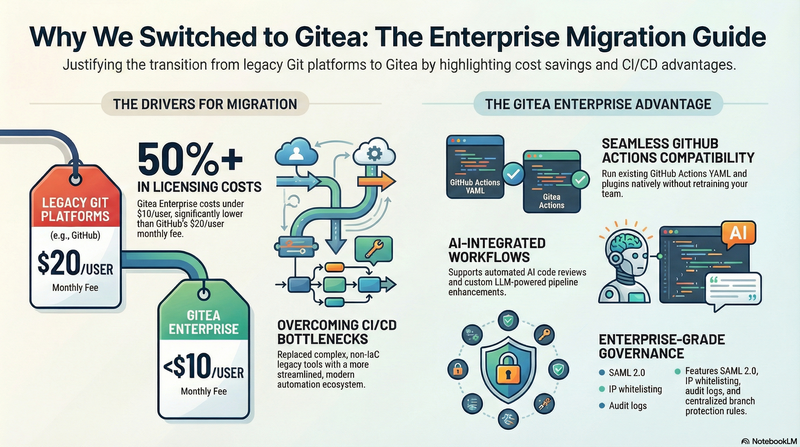
However, for many private companies or small to mid-sized teams, GitHub may not be an option due to security, cost, deployment strategies, or regulatory requirements. In such cases, what tools can serve as an internal Git repository platform? The most common choices include GitLab and Gitea, which is the focus of this article.
For some teams, Gitea might still be relatively unfamiliar. Simply put, Gitea is a lightweight, self-hosted Git platform written in Go, providing GitHub-like capabilities such as code hosting, permission management, Issues and Pull Requests, and CI/CD. You can find a more comprehensive explanation in the official documentation (Gitea Documentation). It’s cross-platform, easy to deploy, and low-maintenance, which is why it has been increasingly favored by small and medium-sized teams.
The main purpose of this article is to share why our team ultimately decided to migrate from Bitbucket Data Center to Gitea—and why we didn’t choose a more feature-rich but comparatively heavier open-source solution like GitLab.
[Read More]